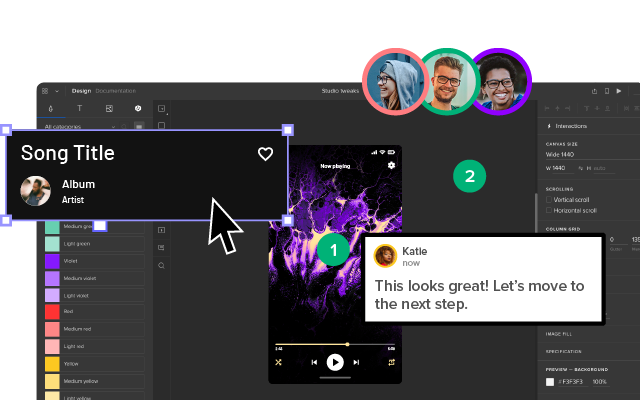
Top Methods of Identifying User Needs
User needs are the specific requirements and expectations of users that a product or service should fulfill to provide value and enhance their experience. These needs represent users’ perspectives, goals, motivations, pain points, and other human factors.
By identifying and addressing user needs, UX designers can create relevant, usable, and possible solutions for the target audience. User needs help define the scope and direction of the product development process, influencing key decisions such as functionality, features, layout, and interaction design.
Understanding user needs also enables designers to prioritize design elements, allocate resources effectively, and make informed design decisions. Make better design decisions with UXPin’s interactive prototypes. Sign up for a free trial to explore UXPin’s advanced features.
Desk research
Desk research (secondary research) is valuable for gathering information and insights to understand user needs based on existing data from various internal and external sources. This data can come from published materials, academic papers, industry reports, social media, online resources, and other third-party data sources.
User interviews
Interviews are a widely used user research method that involves direct conversations with end users to gather insights, understand their perspectives, and uncover their needs.
Researchers ask questions and prompt participants to share their experiences, opinions, and expectations about a product or service. Interviews provide rich qualitative data and allow researchers to delve deeper into users’ thoughts and emotions.
- Structured interviews: follow a predetermined set of questions and a fixed order, allowing for consistency and comparability in data collection. They help gather specific information from participants systematically.
- Semi-structured interviews: offer more flexibility, combining predefined questions with the freedom to explore additional topics and follow up on participants’ responses. This approach encourages participants to express themselves more freely, providing richer insights.
- User story interviews: focus on understanding users’ goals, motivations, and behaviors by having them narrate their experiences through storytelling. These interviews capture the user’s journey and provide valuable context for understanding their needs and expectations.
Surveys and questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are popular user research methods that systematically collect data from many participants. Surveys typically consist of questions designed to gather quantitative or qualitative data about users’ preferences, opinions, behaviors, and demographics.
They provide researchers with a structured approach to gathering insights from a broader audience, allowing for statistical analysis and identification of trends.
- Surveys: allow researchers to reach a wide audience and collect data efficiently, providing quantitative insights. Surveys are beneficial for gathering feedback on specific features, user satisfaction, or demographic information.
- Likert scale questionnaires: use a series of statements or items with response options, allowing participants to rate their level of agreement or disagreement. This method provides researchers with quantitative data to statistically analyze user preferences, perceptions, or attitudes.
Observation and field studies

Observation and field studies are user research methods that directly observe users in their natural environment to gain insights into their behaviors, needs, and experiences.
Researchers can gather rich qualitative data that helps uncover user needs and understand the context in which people use products or services.
- Contextual inquiry: combines observation and interviewing techniques to understand users’ workflows and the context in which they perform tasks. Researchers observe users in their work or living environment and engage in conversations to gain deeper insights into their needs, motivations, and challenges.
- Ethnographic research: involves immersing oneself in the users’ cultural or social context to better understand their behaviors, values, and norms. Researchers spend an extended period with the users, observing and participating in their daily activities, to uncover deep insights that influence design decisions.
- Diary studies: involve participants documenting their experiences, behaviors, or interactions over time. Participants record their thoughts, activities, and emotions in a diary or journal, providing researchers with detailed and longitudinal data. Diary studies offer insights into users’ daily lives, habits, and pain points, helping to identify patterns and uncover unmet needs.
Focus groups

Focus groups are small groups of participants engaging in a guided discussion about a specific topic or product. This method allows researchers to collect qualitative data by leveraging group dynamics and participant interactions.
Participants can share their opinions, ideas, and experiences in a focus group, providing valuable insights into user needs and preferences.
- Plan and conduct effective focus groups by defining clear objectives, selecting appropriate participants, creating a discussion guide, and facilitating the session effectively. Creating a comfortable and inclusive environment encourages participants to express their thoughts and opinions freely.
- Analyze and synthesize focus group data to identify patterns, themes, and key insights. This analysis involves transcribing or reviewing the discussion, extracting meaningful data points, and organizing them into categories. Researchers can use affinity mapping or thematic analysis techniques to make sense of the data and draw meaningful conclusions.
Usability testing
Usability testing evaluates a product or interface’s usability and user experience. It involves observing users performing specific tasks and providing feedback on their interactions. Usability testing helps identify usability issues, understand user behavior, and gather insights for improving the design.
- Moderated usability testing: a researcher facilitates the session and guides participants through predefined tasks while observing their interactions and gathering feedback. The researcher can ask follow-up questions, clarify uncertainties, and delve deeper into participants’ thoughts and experiences.
- Remote usability testing: researchers use video conferencing or screen-sharing tools to observe their interactions and gather feedback.
- Thinking aloud: participants are encouraged to verbalize their thoughts, feelings, and decision-making processes as they navigate a digital product. This narration provides valuable insights into users’ cognitive processes and helps uncover usability issues.
Data Analysis and Synthesis
Data analysis and synthesis is a crucial step in user research that involves organizing, examining, and interpreting the collected data to derive meaningful insights.
Qualitative analysis
UX researchers use qualitative analysis methods to analyze and make sense of qualitative data, such as interview transcripts, observation notes, and open-ended survey responses.
- Thematic analysis involves identifying and categorizing recurring themes, patterns, and concepts within the qualitative data. Researchers review the data, generate codes or labels to represent key ideas, and then group similar codes into broader themes to identify meaningful patterns.
- Affinity diagrams organize qualitative data by grouping related ideas or concepts. Researchers write each finding on sticky notes and then arrange and rearrange them on a wall or board to discover connections and identify patterns or themes.
- Narrative analysis examines the structure, content, and meaning of individual stories participants share. Researchers analyze the storytelling elements, underlying themes, and narrative arcs to gain insights into users’ experiences, perspectives, and motivations.
Quantitative analysis
Quantitative analysis methods analyze numerical data and metrics collected through surveys, questionnaires, and quantitative research studies.
- Statistical analysis applies various statistical techniques to analyze and interpret quantitative data. Researchers use measures of central tendency, dispersion, correlation, and statistical tests to identify data relationships, trends, and patterns.
- Data visualization represents quantitative data using charts, graphs, and other visual representations. Visualizing data helps researchers and stakeholders easily understand patterns, trends, and relationships within the data.
- Pattern recognition helps identify recurring patterns, trends, or anomalies within quantitative data. Researchers look for clusters, outliers, or other patterns that can provide insights into user behavior, preferences, or trends.
Combining multiple methods
Combining multiple research methods enables researchers to validate ideas and identify user needs from various sources, providing more accurate and reliable data.
- Triangulation: Combining multiple user research methods, such as interviews, observations, and surveys, to cross-validate findings and increase the reliability and validity of the data.
- Mixed-methods approach: Integrating qualitative and quantitative research methods, such as combining interviews with surveys or usability testing with analytics, to comprehensively understand user needs and obtain richer insights.
Integrating User Needs into Design
Designers analyze and interpret user research findings to identify specific design requirements that address user needs. These requirements serve as guidelines for the design process, ensuring that the resulting solutions align with user expectations and user-centered design principles.
Designers create several documents and visualizations to guide the design process, including user need statements, personas, case studies, and other UX artifacts.
Design teams also meet with stakeholders to integrate business goals and user needs. They must consider user feedback, conduct usability testing, and incorporate iterative feedback loops to achieve the right balance. This iterative approach allows designers to continuously refine their solutions based on user needs, preferences, and feedback.
Advanced Prototyping and Testing With UXPin
UXPin’s advanced prototyping features enable design teams to build accurate replicas of the final product. These fully interactive prototypes allow designers to observe and analyze user behavior, preferences, and pain points, validating whether designs effectively address user needs.
Users and stakeholders can interact with user interfaces like they would the final product, giving designers meaningful, actionable insights to iterate and improve.
Whether you’re a startup looking to validate a new product idea or an enterprise team looking to scale your DesignOps, UXPin has a solution for your business. Sign up for a free trial to explore the world’s most advanced UX design tool.